Choice of Model Metrics
Precision vs Recall Model
Misclassifications (notified on predicted value)
- False Positive = detected positive, wrongly
- False Negative = detected negative, wrongly
Examples of wrong outcomes:
- If an important mail is detected spam positive (FP), it is a bad outcome
- If a cancer patient is detected cancer negative (FN), it is a bad outcome
We want to reduce the no of bad outcomes. To reduce the no of bad outcomes, we need the bad outcomes in the denominator.
Hence to decide whether to use a precision or recall model, decide which is a bad outcome. Then put the bad outcome in the denominator and
High Precision models are used when we need to reduce the false positives ie when its a spam model where we are okay with classifying something as
High Recall models are used when we want to decrease the false negatives ie when a person is not diagnosed but they have the disease.
Precision and Recall are inversely proportional. ie if Precision increases then recall decreases.
Bias vs Variance Model
Bias: how much on average is my predicted values different from actual values. High bias is underfitting.
Variance: how different will predictions be, at the same point, if different samples are taken from the same population. High variance causes overfitting.
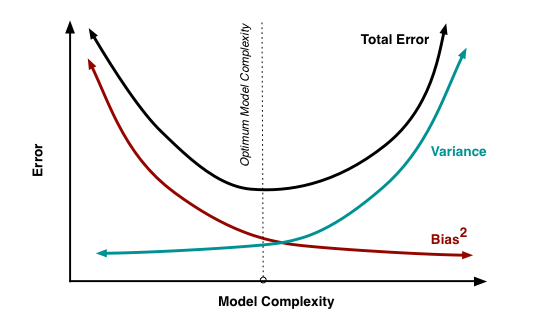
Bias - Variance Tradeoff
- high bias = high (pred - act) = high error = underfit model
- high variance = high sensitivity in changes in data = overfit model
When a model has high bias, this means that it doesn’t do a good job of bending to the data
When a model has high variance, this means that it changes drastically to meet the needs of every point in our dataset
High Bias, Low Variance models tend to underfit data, as they are not flexible. Linear models fall into this category of models.
High Variance, Low Bias models tend to overfit data, as they are too flexible. Decision trees fall into this category of models.
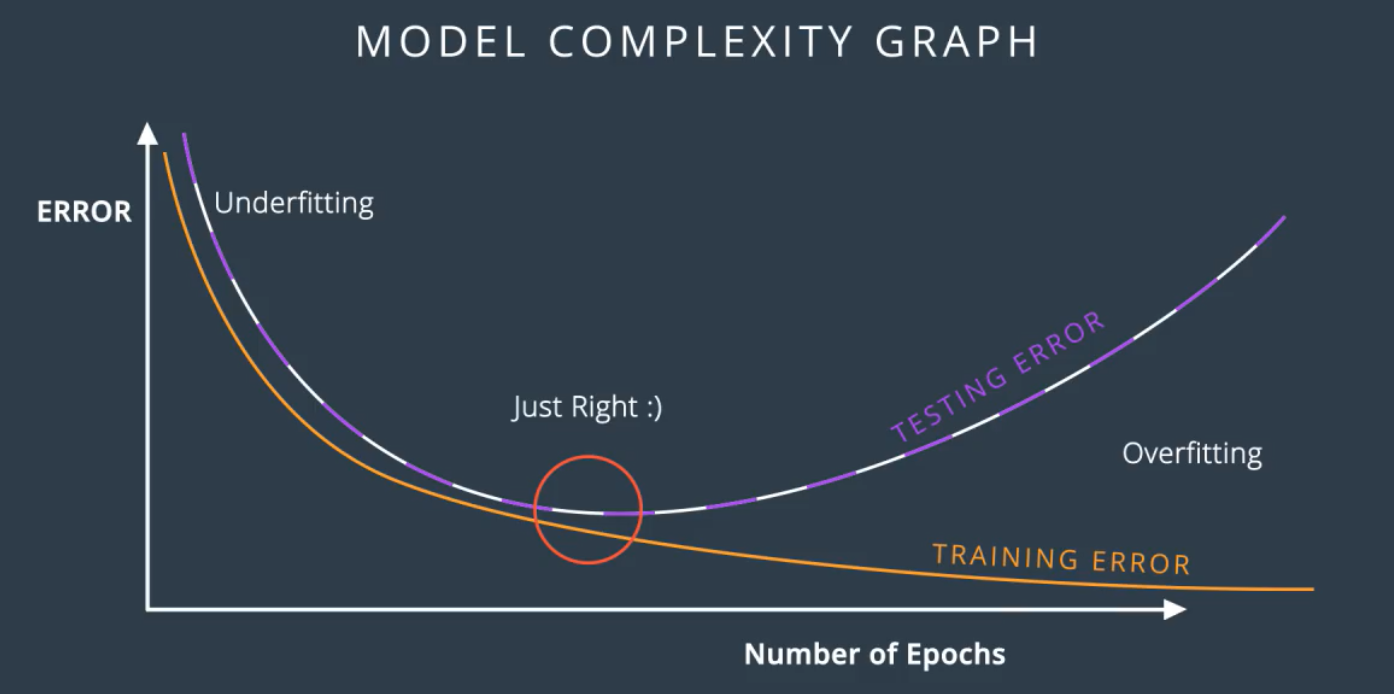
Model Complexity Graph : Plots the training and testing error and helps find the optimal point between underfitting and overfitting.